The Digital Divide: Examining the Drawbacks of Online Applications
Related Articles: The Digital Divide: Examining the Drawbacks of Online Applications
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Digital Divide: Examining the Drawbacks of Online Applications. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Digital Divide: Examining the Drawbacks of Online Applications

The advent of online applications has revolutionized the way we interact with the world. From banking to shopping, education to healthcare, the convenience and accessibility of digital platforms have become ubiquitous. However, beneath the surface of this digital revolution lie inherent drawbacks that warrant careful consideration. This article explores the challenges posed by the increasing reliance on online applications, highlighting their potential limitations and negative impacts.
Accessibility and Equity:
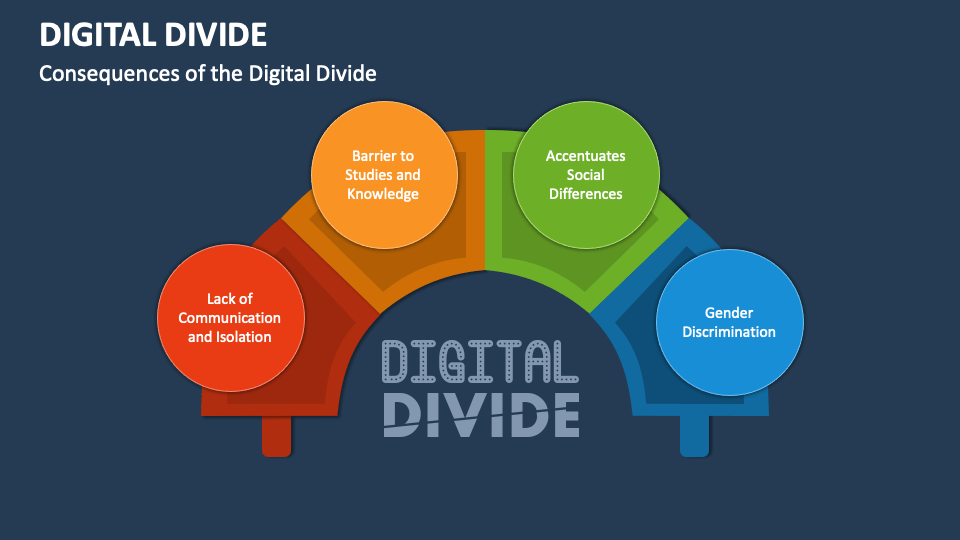
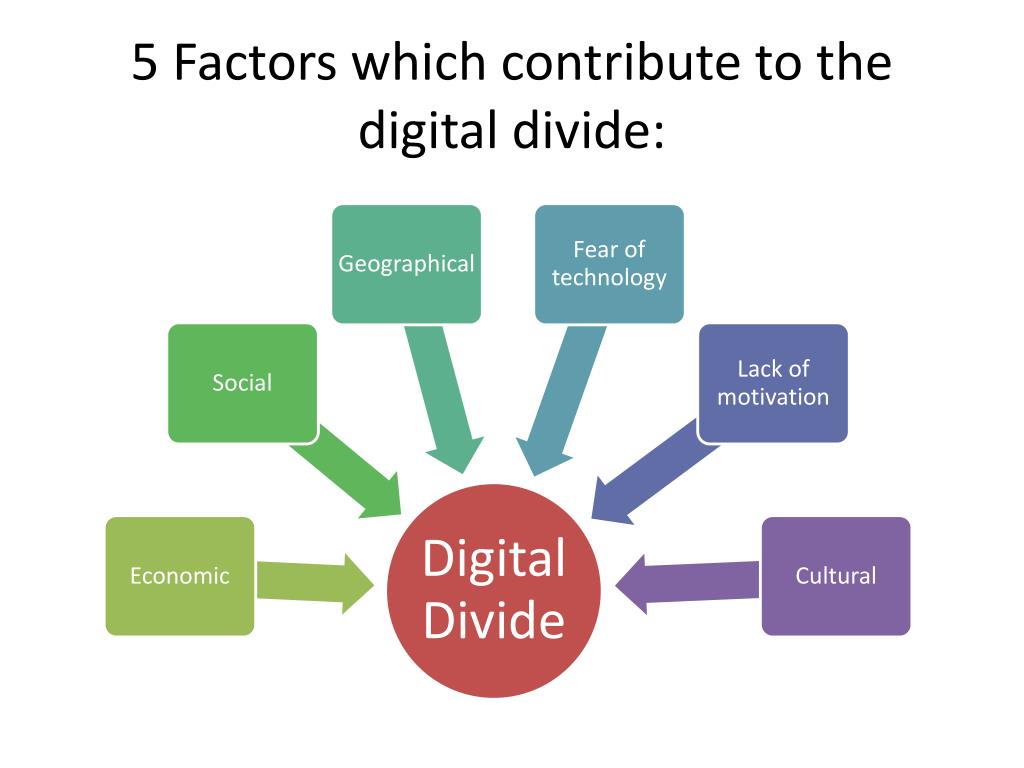
The first significant drawback of online applications is their inherent dependence on digital infrastructure and literacy. While the digital world offers unprecedented access to information and services, it also creates a stark digital divide. Individuals lacking reliable internet access, appropriate devices, or sufficient digital literacy skills are effectively excluded from the benefits of online applications. This creates a disparity in opportunity and access to essential services, particularly impacting vulnerable populations such as the elderly, low-income individuals, and those residing in rural areas.
Data Security and Privacy:
Online applications necessitate the sharing of personal data, raising concerns about security and privacy. Data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized access to sensitive information are constant threats. The complex and interconnected nature of online systems makes it difficult to ensure complete security, leaving individuals vulnerable to exploitation. Moreover, the collection and use of personal data by companies and governments raise ethical dilemmas regarding data ownership, surveillance, and the potential for misuse.
Digital Fatigue and Mental Health:
The constant connectivity and stimulation offered by online applications can lead to digital fatigue and negatively impact mental health. The constant barrage of notifications, the pressure to stay connected, and the fear of missing out can contribute to anxiety, stress, and sleep deprivation. The blurring of boundaries between work and personal life further exacerbates these issues, leading to burnout and decreased well-being.
Digital Dependency and Skill Erosion:
The reliance on online applications can lead to a decline in essential skills and knowledge. For instance, the widespread use of GPS navigation systems can diminish spatial awareness and navigation abilities. Similarly, reliance on online calculators and spell checkers can erode mathematical and linguistic skills. This digital dependency can hinder critical thinking, problem-solving, and the development of essential life skills.
Social Isolation and Community Weakening:
While online applications facilitate communication and connection, they can also contribute to social isolation. The convenience of virtual interactions can lead to a decline in face-to-face interactions, weakening social bonds and community cohesion. This isolation can have detrimental effects on mental health, social development, and the ability to build meaningful relationships.
Job Displacement and Economic Disparity:
The automation and digitization enabled by online applications can lead to job displacement in certain sectors. As machines and algorithms take over tasks previously performed by humans, workers may find themselves facing unemployment and economic hardship. While new opportunities may emerge, the transition can be challenging, requiring retraining and adaptation to new skill sets. This can exacerbate existing economic disparities and create social unrest.
Manipulation and Misinformation:
Online applications are susceptible to manipulation and the spread of misinformation. Algorithmic biases, targeted advertising, and the spread of fake news can distort perceptions, influence opinions, and erode trust in information sources. This can have far-reaching consequences, impacting political discourse, social cohesion, and individual decision-making.
Environmental Impact:
The production, use, and disposal of digital devices and the vast infrastructure required to support online applications have significant environmental consequences. Data centers consume enormous amounts of energy, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. The mining of rare earth minerals for electronic devices also raises ethical and environmental concerns.
FAQs by Drawbacks of Online Applications:
Q: How can I protect my data privacy while using online applications?
A: Employ strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, be cautious about sharing personal information, and regularly review privacy settings on your devices and applications.
Q: What can be done to address the digital divide and promote digital literacy?
A: Governments and organizations should invest in expanding internet access, providing affordable devices, and offering digital literacy programs to bridge the gap in access and skills.
Q: How can I manage digital fatigue and protect my mental health?
A: Set limits on screen time, prioritize sleep, engage in offline activities, and practice mindfulness techniques to manage stress and maintain a healthy balance.
Q: Are there any benefits to the increased reliance on online applications?
A: While drawbacks exist, online applications offer significant benefits, including increased access to information and services, enhanced communication, and improved efficiency in various sectors.
Tips by Drawbacks of Online Applications:
- Be mindful of your online activity: Limit screen time, prioritize offline interactions, and take breaks from digital devices.
- Protect your data: Use strong passwords, enable two-factor authentication, and be cautious about sharing personal information.
- Develop essential skills: Engage in activities that promote critical thinking, problem-solving, and creative expression.
- Support digital literacy initiatives: Advocate for increased access to technology and digital literacy programs for all.
- Promote ethical data practices: Support organizations working to protect data privacy and promote responsible data collection and use.
Conclusion by Drawbacks of Online Applications:
The widespread adoption of online applications has undeniably transformed our lives, offering unprecedented convenience and access to information. However, it is crucial to acknowledge and address the inherent drawbacks that accompany this digital revolution. The accessibility and equity challenges, data security and privacy risks, and potential negative impacts on mental health, social cohesion, and the environment require careful consideration and proactive measures. By promoting digital literacy, fostering ethical data practices, and embracing a balanced approach to technology, we can mitigate the drawbacks of online applications and harness their potential for positive societal change.





.png)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Digital Divide: Examining the Drawbacks of Online Applications. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!